Participation in Research and Extension Endeavors
According to the Republic Act (RA) No. 8292 also known as the “Higher Education Modernization Act of 1997” mandates the governing board of the State Universities and Colleges (SUC) to establish research and extension centers to promote the development of the latter (Section 4-m). In addition, pursuant to RA No. 7722, and as reiterated in Commission on Higher Education (CHED) Memorandum Order No. 52, Philippine higher education institutions (HEIs) need to become platforms for research, innovation, and extension in pursuit of inclusive social and economic development. Hence, faculty members need to conduct research activities and participate in extension activities.
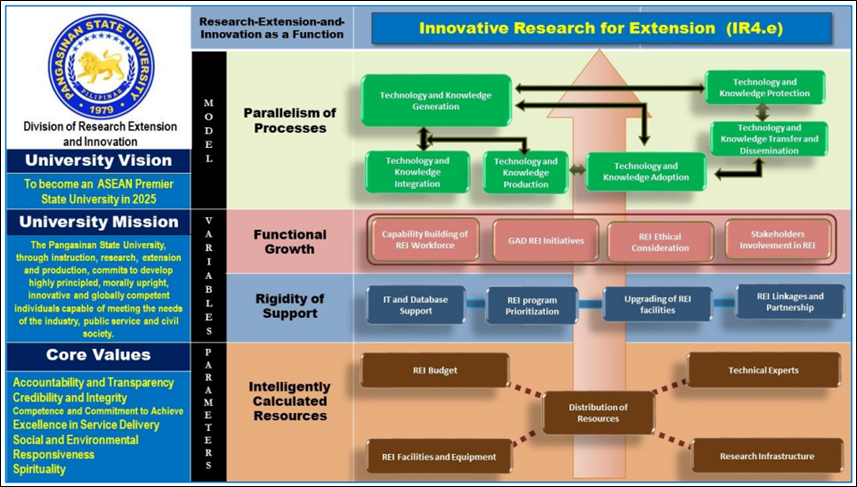 Perspective of the Research, Extension, and Innovation (REI) Strategic Development Plan
Perspective of the Research, Extension, and Innovation (REI) Strategic Development Plan
As a matter of fact, two of the four core functions present in Pangasinan State University are Research and Extension. These two functions are strongly associated with respect to each other, that is, research activities are interdependent with extension activities. Indeed, the University continuously provides high support and encouragement to its employees, whether in teaching or non-teaching fields, to participate in research and extension activities by providing avenues to present research and extension proposals, financial support, service credit incentive, and awards.
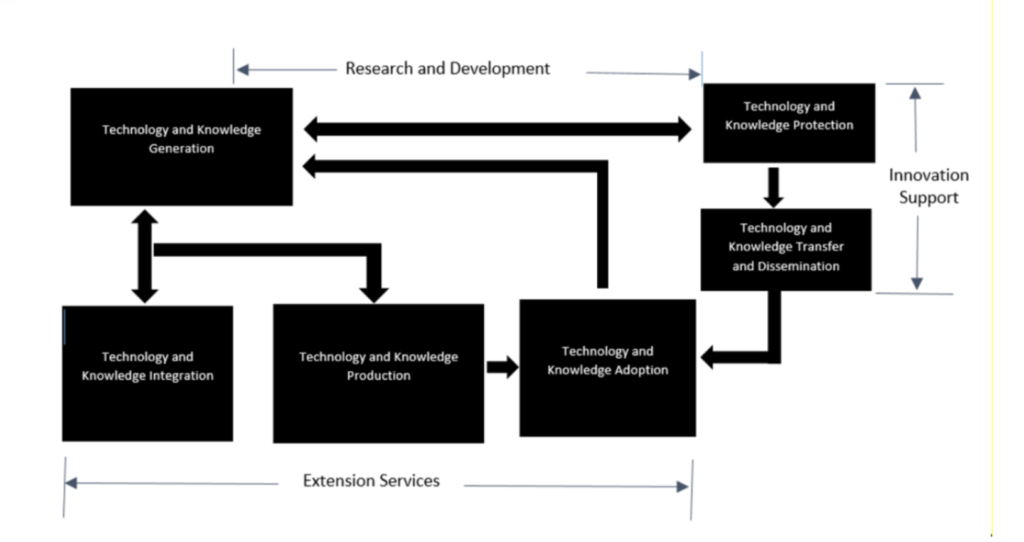
Model of the REI Process
Research and Extension Processes
The process starts with the formulation of the researchable areas under different priority programs anchored on the University RDE Agenda which will be undertaken by the Vice President for Research, Extension and Innovation Support (VP-REIS), together with the Director for Research, Director for Extension, Director for Innovation Support and Center Heads. The VP for REIS shall present these priority programs to the University President and the BOR Research Committee for discussions and finalization of priority researchable areas.
Formulation of researchable areas, dissemination, and proposal writing
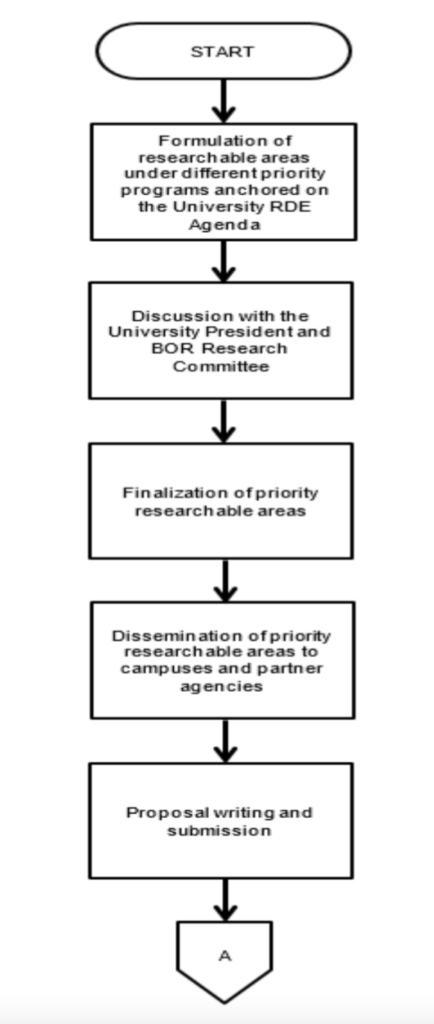
Dissemination of priority researchable areas to all the campuses and units in the University will be done through an office advisory released by the University President. The Research Council is also tasked to disseminate these priority researchable areas to stakeholders including students, faculty, academic support staff, and prospected partner agencies.
A call for proposal submission will be announced through an official advisory. Faculty researchers and academic staff may start writing and submitting their proposals to their Campus Research and Extension Coordinators. These proposals will be submitted to the Campus Executive Directors/ Executive Directors who shall endorse to the Office of the VP-REIS. Initial review and classification of research proposals will be done by the three Directors and the VP-REIS.
Review and classification of research proposals into specific RDE centers
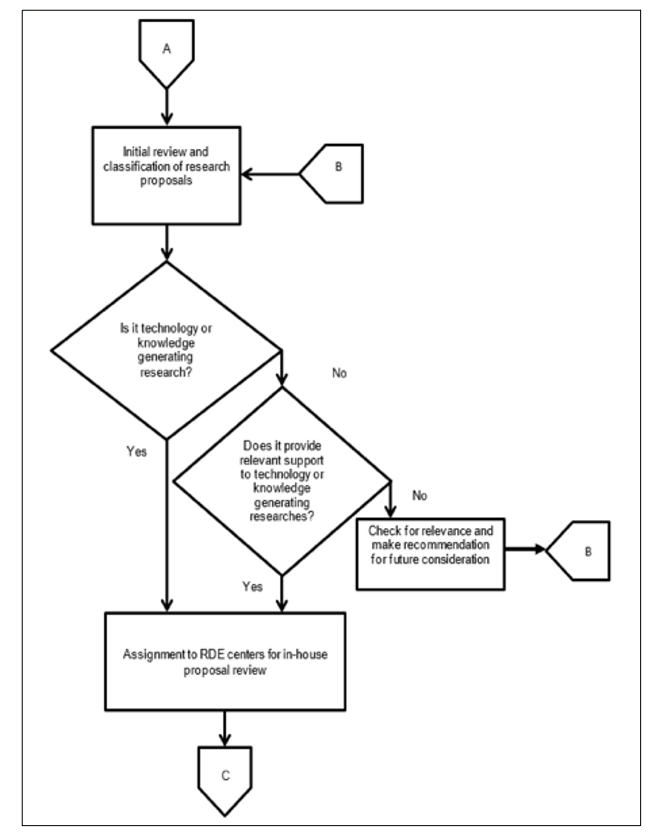

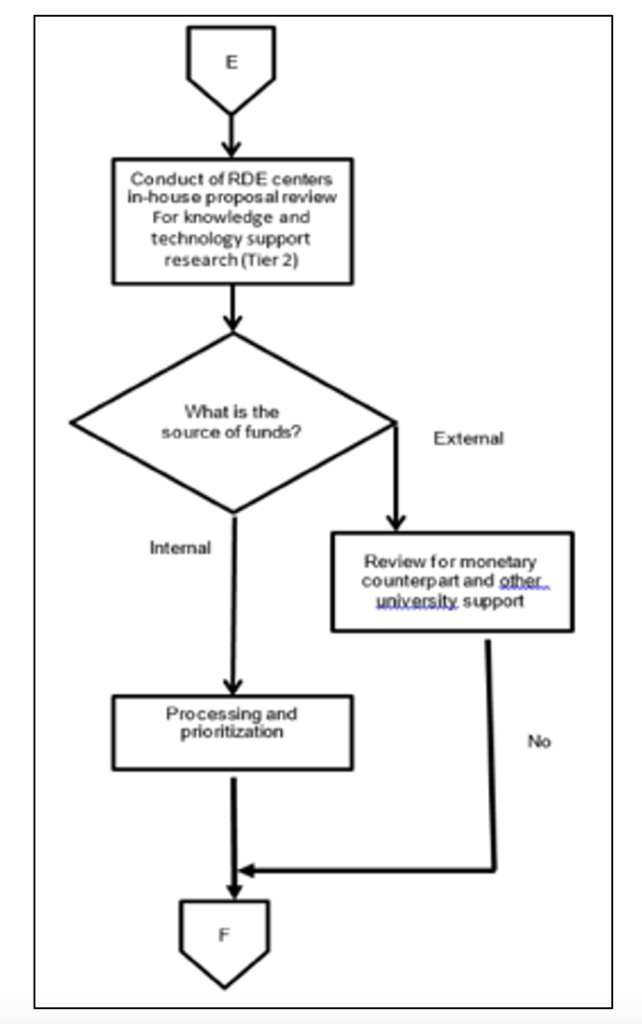
In the evaluation of these proposals, an important question being raised is: Is it technology or knowledge-generating research? If yes, the proposals will be assigned to RDE centers for in-house proposal review. If not, the research must be generating relevant support to technology or knowledge-generating research for it to be endorsed for the in-house proposal review.
The in-house proposal review per Research Center will be scheduled. The research program/project/ study leader has to present his/her proposal before the panel members composed of the VP-REIS, Directors, Center Heads, internal and external experts.
The panel members shall evaluate, review and filter the proposals presented. Another consideration is the means of funding of the research and extension proposal. If it is for internal funding, the Research Council shall endorse these selected proposals for funding. For external funding, the monetary counterpart of the University or other support will be reviewed.
After the in-house proposal review of all the Research Centers, the VP-REIS shall disseminate the shortlisted titles to the campuses through an official advisory. For the approved externally-funded research, a MOA will be agreed upon by PSU and the funding agency. The MOA shall be presented to the BOR for approval.
Fund will be requested for the implementation of the approved research proposal from the University for internally funded proposals; while, funds for externally funded may be requested from the University if funds are already downloaded to PSU coffers. Research progress monitoring and reporting shall be done. The researchers are required to submit a monthly and quarterly progress report to their Campus Coordinators, who will classify for which Research Center each research progress report will be forwarded. And once the research is completed, the researcher has to submit terminal reports. Now, in case the research is not completed on time, the concerned Research Center through its Monitoring and Evaluation Unit shall review the risks or problems encountered by the researcher/s and offer solutions or corrective actions in the process.
Research creation and completion
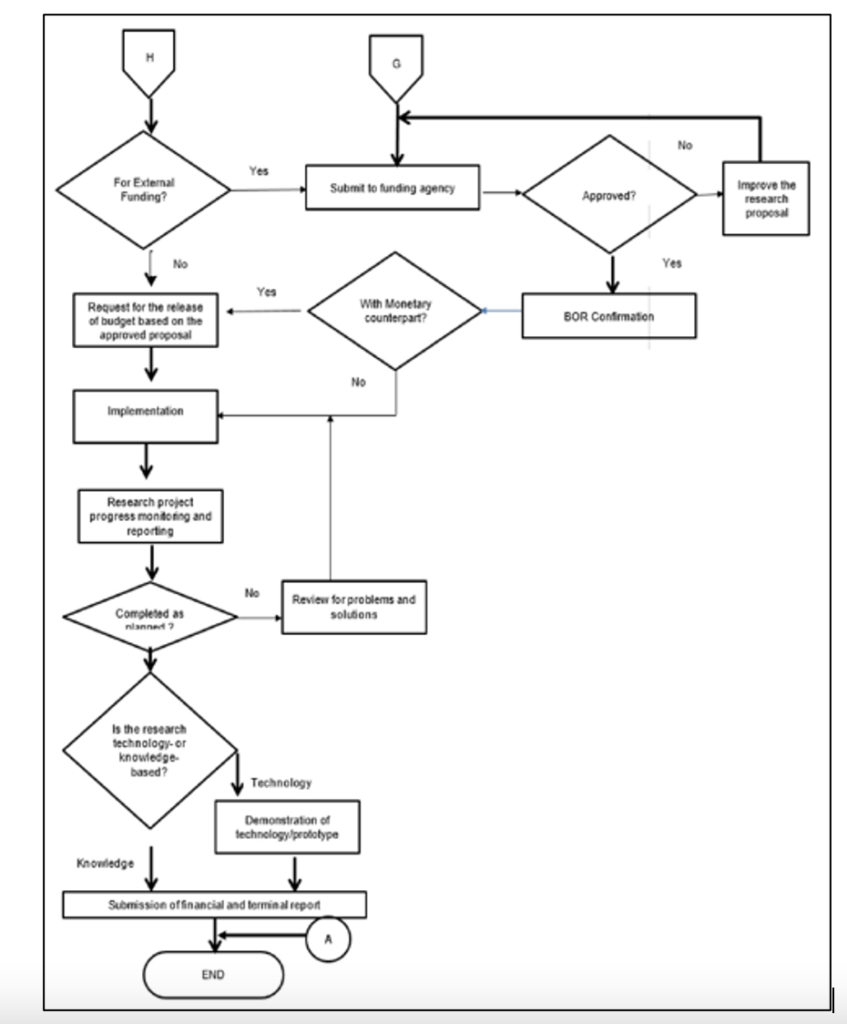
If the completed research generates knowledge, the concerned Research Center shall determine its utilization. If the research generates technology, such will be endorsed for its protection and the development of a prototype for production.
(PSU-REI Manual, pp. 30-37)
Research and Development Credit and Incentive
The minimum regular teaching load for faculty members performing research and development activities is 8 hours per week with 2 preparations. Faculty members are eligible for service credit incentives if they are assigned more units than the minimum regular teaching load. Every research and extension activity that faculty members participate in is credited and rewarded appropriately. In addition to his or her teaching load, a faculty member may perform three (3) research studies, one (1) research project, or (1) one program at a time. Coworkers in one or more studies, projects, or programs will distribute the unit load proportionally based on their level of participation. The credit is as follows:
| Type | Amount | Conditions for Reward |
| Study | 3 units/semester/study | 12 months (7 days service credit) |
| Project | 6 units/semester/project | 1 year and 2-3 studies (14 days service credit) |
| Program | 9 units/semester/program | at least 2-3 years and 3 or more studies (21 days service credit) |
Moreover, the project/program leader is required to produce an annual update report on the status of the program/project, as well as a financial report. If deloading is not possible because of the scarcity of faculty members, equivalent service credits are given instead.
| Equivalent Service Credit | |
| 3 units | 7 days |
| 6 units | 14 days |
| 9 units | 17 days |
At the beginning of the research, the proponents will be given a special order to designate themselves as study leader, project leader, or program leader. Professors should be in charge of the research program, which should be externally funded.
(PSU-R&D Manual, p. 85)
The Extension Processes are involved in various activities such as the dissemination and transfer of knowledge and technology, and the utilization and adoption of knowledge and technology.
Process of Dissemination and Transfer of Knowledge and Technology
This process centers on the dissemination and transfer of knowledge from University to the target clientele. It starts with the submission of complete terminal report and will be presented during the forum and open for suggestions or comments to be incorporated so to improve the quality of the output. The improved output can be presented in local, provincial/regional, national or international in a form of publication and oral presentation after applied protection. The Extension services or Technology Transfer Office (TTO) will identify the objects ready to be transferred, this transfer objects are classified as IPR’s (patents, utility model, or industrial design) and the office also determine the objects its commercial viability. If the transfer object does not have commercial value but maybe useful in the community are nonexclusively transferred to other parties via Memorandum of Agreement.
The TTO/Researcher will provide relevant information/ documents like reference materials to facilitate promotion, dissemination, transfer or commercialization of the IP’s/IPR’s to prospective adaptors. The university has the right to commercialize any potential IPR generated within a year it was granted, but the inventor/author/designer shall be allowed to commercialize or participate in a spin-off company subject to the provision of R.A. 10055. However, the University shall have all the right to the IP and take over the commercialization. Refer to Technology Transfer Protocol of the University for more information.
Pitching session, exhibits or caravans, professional meetings and publish list of technology through IP depot at IPOPHL are some ways to find prospect technology adopters and investors. From that potential adopters or investors will write a letter of intent, negotiate, and consider the projected cost, valuation and other business transactions. Craft the fairness opinion report (FOR) and present to the Fairness Opinion Board at DOST for certification and clearance. Technology Licensing Agreement (TLA) will be draft from the TTO and present to the prospective technology adopter for review and finalization, from there explain the necessary payment stipulated in the TLA to the University cashier. The TTO will conduct necessary training and technical assistance to the adopter in the initial stage of incubation/commercialization, followed by ex-post analysis/impact assessment three years after technology or knowledge transfer.
(PSU-R&D Manual, p. 50)
Process of Utilization and Adoption of Knowledge and Technology
The process of technology and knowledge utilization and adoption starts with the Extension Services Division which reviews the results of training-workshop or series of workshops on mature technology conducted by the University. Target adopters are then assessed whether to use or not to use the PoT based on its perceived usefulness and ease of utilization.
Once decided, the target adopter, with the help of the Extension Services Division and the PoT generator will access the capability of the target adopter on the resources needed to use the technology. If the resources needed are not available, target adopter may source out the needed resources. Target adopters will initially utilize technology under trial. Continuous trials will be made until all expectations are made following necessary adjustments before another trial is to be conducted. Once satisfied with the trials, target adopter will adopt the technology subject to some agreed rules on the adoption.
Monitoring and evaluation will be conducted throughout the adoption period of the PoT to address possible issues and concerns and for improvement. At least three years after adoption of PoT, the Extension Research Monitoring and Evaluation Unit will conduct impact assessment.
(PSU-R&D Manual, p. 56)
Extension Rewards System
An approved reward system shall be given to recognize and compensate the involvement of the faculty members in extension activities.
Section 1. Every member of the academic and non-academic staff shall be encouraged to engage in extension activities and such activities should form part of the merit promotion plan.
Section 2. The reward to be given to a faculty-extensionist shall be based on the approved policy guidelines on de-loading and incentives.
GUIDELINES FOR ACADEMIC DE-LOADING AND INCENTIVES FOR FACULTY-EXTENSIONISTS
- The de-loading shall be given to a faculty member who has an approved extension project for implementation. The approved designation shall be attached when requesting for de-loading and incentives.
- The de-loading of faculty members involved in extension projects shall be done during the semester(s) when the Extension proposals are approved for funding and implementation.
- The number of academic load to be reduced depends on the nature of involvement in an approved extension activity.
- Failure to conduct and implement the approved Extension activities/and or non- submission of the progress report will deprive the faculty member from de-loading and incentives for the next or ensuing semester. He/she shall be given full teaching load without the benefits of overload to offset the privilege enjoyed the previous semester.
- For extension projects with outside funding and with an approved honorarium, a copy of the approved Extension project must be submitted to the Office of the Vice President for Research and Extension for proper recording. No de-loading privilege shall be given to the faculty extensionist involved.
- The academic load equivalent or incentive per involvement in extension project as follows:
- In case where de-loading is not possible, the equivalent compensatory leave credit shall be given to the faculty based on the approved unit load equivalent of the involvement in extension project.
- The granting of monetary incentives to faculty members who have published extension papers in acceptable/reputable journal shall be categorized and be given the following cash incentives: The granting of cash incentive is per study/project/program. The cash incentive shall only be claimed once regardless of the number of publications.
On Membership to Professional Organizations
The Pangasinan State University gives freedom to its employees to choose professional organizations especially when it is in the same fields in which they teach. This is to be updated on the current breakthroughs and opportunities and to meet other professionals for possible collaborations. This provision is further discussed in the items below:
C.2.a The faculty member can join professional organizations related to the area of specialization on their own initiative.
C.2.b The administration supports the active membership of the faculty members by allowing the faculty member to attend to conferences, seminars, and trainings sponsored by the professional organizations on official business and providing financial assistance following proper accounting rules and procedures and liquidation of funds.